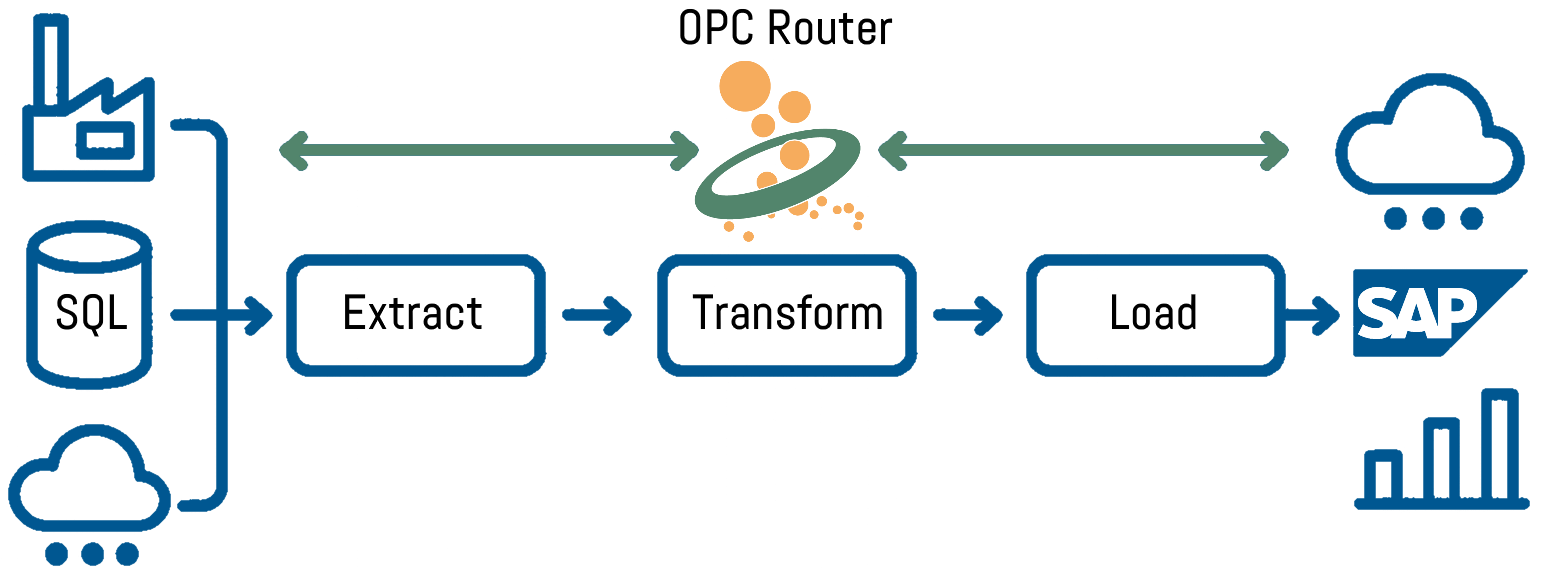
ETL: Extract, Transform, Load
ETL stands for Extract, Transform, Load and is a central data management process. ETL involves collecting data from various sources, preparing it and transferring it to its destination. Here, the data is first extracted from its original sources (Extract), then converted into a more comprehensible form (Transform) and finally loaded into the target system (Load). This automatically turns raw data into clear, structured and directly analysable information.

Table of contents
ETL: Extract, Transform, Load
ETL stands for Extract, Transform, Load and is a central data management process. ETL involves collecting data from various sources, preparing it and transferring it to its destination. Here, the data is first extracted from its original sources (Extract), then converted into a more comprehensible form (Transform) and finally loaded into the target system (Load). This automatically turns raw data into clear, structured and directly analysable information.

Table of contents
1. ETL in practice: moving data intelligently
In a world in which everything is increasingly networked, ETL is not just a topic for IT. It has also become an important building block for modern industrial and IoT applications. In the industrial environment, data is generated in a wide variety of places. Machines, controllers, sensors and ERP systems continuously supply information. However, this data only realises its value through structured processing. This is exactly where the ETL process comes into play:
Extract: Data is extracted from various source systems, e.g. SQL databases, REST APIs, OPC UA servers or MQTT brokers.
Transform: The extracted data is standardised, calculated, converted or enriched. This is done, for example, by converting units, mapping codes or merging multiple data sources.
Load: The processed data is transferred to ERP systems such as SAP or Oracle NetSuite, to business intelligence platforms (BI) or to cloud services, for example.
2. the OPC router as a powerful ETL platform
The OPC Router is a modular and scalable solution that tailors the ETL process precisely to industrial applications. As middleware, the OPC Router enables the simple creation of complex data flows without any programming effort.
– Extraction from e.g. OPC UA, MQTT, SQL, REST, SAP, …
– Transformation using integrated logic modules (scripting, calculations, data mapping)
– Loading into various target systems, on-premise or in the cloud
The OPC Router’s graphical drag-and-drop editor simplifies the design of ETL routes and makes complex processes visually comprehensible.
Example: Saving temperature data from production in SAP
A practical ETL scenario with the OPC router:
Requirement:
Temperature values from production systems are to be read out cyclically, checked, converted into °C and then stored in the SAP system for quality documentation.
Realisation with OPC Router:
– Extract: The OPC UA plugin reads the raw temperature values (e.g. in Kelvin) directly from the PLC.
– Transform: The conversion from Kelvin to Celsius is carried out via a calculation field in the connection editor. A further module then checks whether the values are within a defined tolerance range.
– Load: If the measured values are valid, an IDOC is automatically sent to the SAP system, which posts the temperature values as batch information.
This example shows how a complete ETL process can be realised in an automated, traceable and scalable manner with just a few clicks.
3. ETL meets scaling
In modern Industry 4.0 scenarios, data volumes, data sources and analysis requirements are constantly increasing. To cope with this complexity, you not only need a well thought-out ETL strategy, but also a scalable platform.
The OPC Router enables scalable data integration through the distributed operation of multiple instances. Either locally in production or across multiple locations. This means that your data architecture remains performant and flexible even with growing data volumes.
4. intelligent ETL processes with the OPC router as MCP server
From Data Source to AI-Powered Decision Making
The combination of OPC Router and MCP (Modular Control Protocol) opens up completely new possibilities for controlling powerful, automatic ETL processes directly in production. While OPC Router handles data transfer between machines, controllers, databases, and business systems, it can also become a powerful tool as an MCP server, providing AI language models (LLMs – Large Language Models) and chat assistants with real-time Industry 4.0 machine data, for example on edge devices directly at the production line. This close collaboration enables ETL processes to be executed close to the data source, reducing latency and saving bandwidth. The collected and processed data can then not only be forwarded to ERP, MES, or BI systems, but also analyzed in real-time by AI models. This creates a continuous data chain – from the machine through processing to intelligent predictions.
The OPC Router as the basis for AI in production
Particularly in Industry 4.0 environments, where quick decisions about product quality, maintenance, or energy consumption are required, this architecture provides the perfect foundation for AI-based solutions. The OPC Router plays the key role here: It organizes, structures, and makes data from various sources available – the foundation for machine learning, predictive maintenance, and smart automation. With this solution, ETL becomes not just a tool for data integration, but a strategic building block for future-proof, data-driven production.
Want more information about AI integration? MCP and OPC Router: How Your Language Model Understands Industry 4.0
5. Conclusion: ETL as the Backbone of Industrial Data Integration
ETL is an essential concept for efficient data processing in industry. The OPC Router not only makes ETL accessible, but also practically implementable through modular connectivity, simple configuration, and high scalability. This transforms distributed data sources into an integrated information foundation for well-founded decisions, automation, and digitalization.
6. Micro-FAQ for “What is ETL?”
- What does ETL mean?
ETL stands for Extract, Transform, Load. It describes a data process in which information is extracted from different sources, transformed into a unified format, and then loaded into a target system such as a database or data warehouse.
- What steps are included in an ETL process?
A classic ETL process consists of three phases:
1️⃣ Extract: Data is collected from various sources (e.g., ERP systems, machines, cloud services).
2️⃣ Transform: The data is cleaned, standardized, and converted into the required target format.
3️⃣ Load: The processed data is loaded into a target system, e.g., a database or a dashboard. - What is ETL used for in companies?
ETL is used to combine data from different systems and make it centrally accessible. Companies use ETL for reporting, business intelligence, production monitoring, or the integration of SAP and other ERP systems.
- What is the difference between ETL and ELT?
In classic ETL, data is transformed before being loaded.
With ELT (Extract, Load, Transform), the data is loaded into the target system first and transformed there in a last step – often used in modern cloud architectures. - Are there more than 3 phases in ETL?
The traditional ETL model always comprises three main phases: Extract, Transform, and Load. In practice, however, these steps are often subdivided more granularly to better represent complex processes.
Examples of additional intermediate steps:
- Data Discovery – identifying and selecting data sources
- Data Validation – checking raw data before transformation
- Data Quality Checks – ensuring quality before data enters the target system
Important: These additional steps are not new core phases, but rather detailed breakdowns of the three classic ETL steps. ETL remains a 3-phase principle, but can be represented more granularly in practice to plan and control processes more cleanly.
Which questions do you have about ETL?
More information
Find out what middleware is and how it can help your company. In our “What is middleware?” article, you will learn all about how it works, its advantages and areas of application in practice.
MariaDB or MySQL are just two of many possible database types. Both databases are very popular in practice, which means that users often weigh up which database might be more suitable for their use case. This raises the question: Is MariaDB actually the better MySQL for many people? We will show you which database solution is the right one for your company.
Read how the use of inray’s OPC Router at bicycle manufacturer corratec creates reliability and avoids downtime. The OPC Router creates more transparent data transfers from the ERP system to the control level.
You can find more interesting articles on the topics of Industry 4.0, cloud, technology, alerting and practical application examples as well as case studies in our knowledge base.