The document-oriented database impresses with its performance and high horizontal scalability
What is MongoDB? MongoDB is a database based on a non-relational document model. Thus, as a so-called NoSQL database (NoSQL = Not-only-SQL), it differs fundamentally from conventional relational databases such as Oracle, MySQL or the Microsoft SQL Server. The name MongoDB is derived from the English word “humongous”, which roughly means “gigantic”. MongoDB was released in 2009 by founder and developer Eliot Horowitz, who stepped down as Chief Technology Officer and from the Board of Directors of MongoDB Inc. in 2020, but is still active as a technical consultant.
You can find a special video with the caption “connection of database systems” on this topic in our tutorial stream.

1. Database use in the industrial environment
The conceptual differences of the document-oriented NoSQL database MongoDB to conventional SQL databases can be explained in the following example.
In a sales office for plastic parts, a relational database is used for customer management, which stores the customer data there, for example, as in an Excel table consisting of rows and columns. Let’s first look at a small part of this system, the contact information for the customers. It could start with a simple table that contains one row for each customer. This row has a unique customer ID number, a first and last name, email address, phone number and company address.
Now what if we might want to add a second phone number for a customer?
For a work number and a mobile number or even an emergency contact number, we could simply add more columns. The same problem could arise with multiple addresses, for example if a client wants a sample sent to their home office. Also previous addresses or information for a preferred special colour for the plastic parts could be information you might still need. You now simply add more columns for all the customer’s contact information. Eventually you will end up with a bloated, mostly empty, inefficient table as many fields are unused for many other customers.

Instead, of course, new spreadsheets could be created in our Excel model if additional data is needed. So here a new separate sheet for telephone numbers, which contains only one telephone number in each row, which refers to the customer ID and is marked with a label like “Private”, “Work” or “Mobile”. Another sheet can be created in this way for addresses and so on.
One would create a multitude of sheets just to look at a single customer and here no thought has even been given to order history or invoice filing. You can guess how quickly working in this rigid schema can get out of control. However, this is how developers work with data in these relational, table-based databases in real applications.
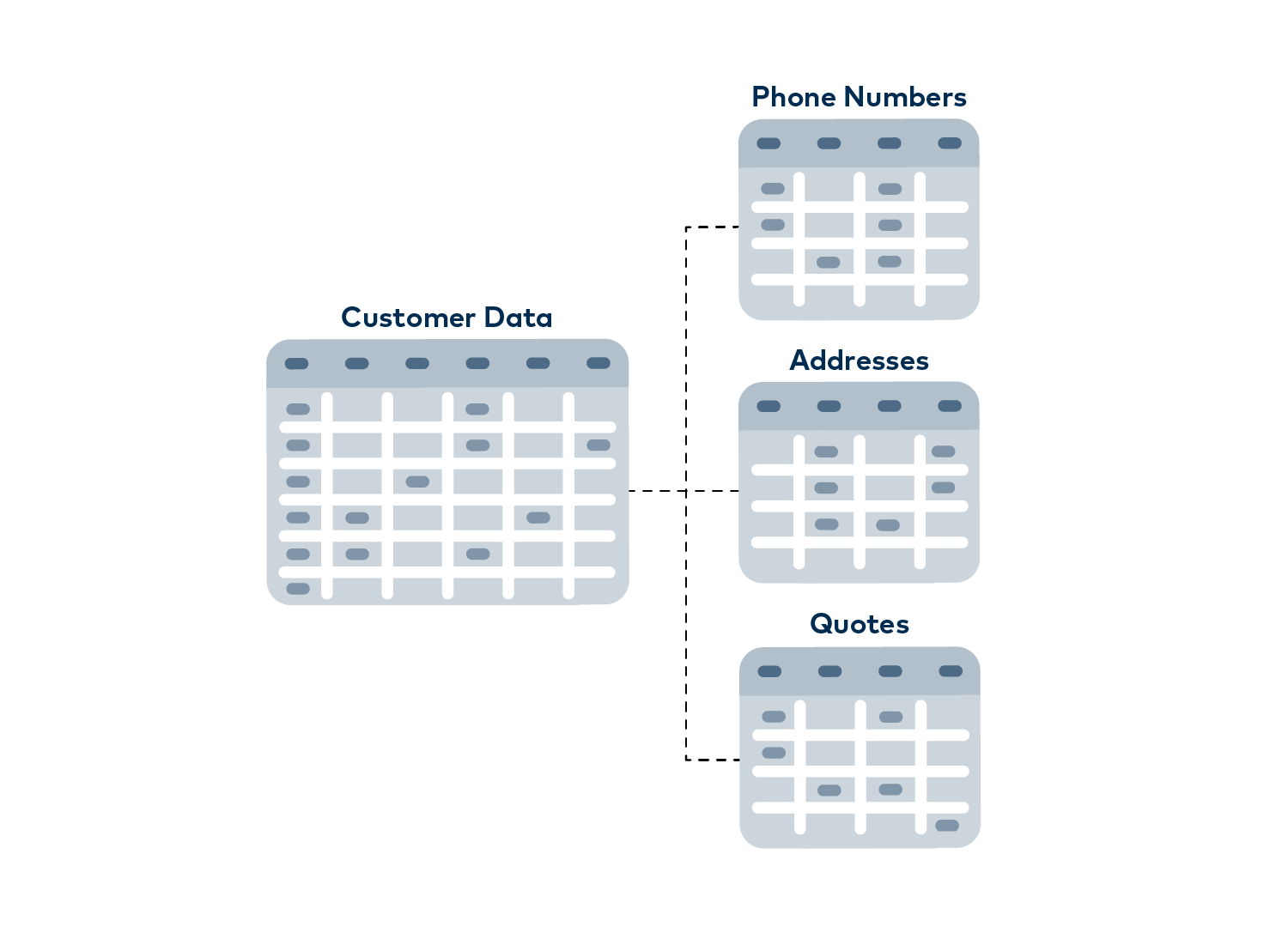
1.1 Data in a relational database
The data for a single thing, like a customer, is often spread over dozens of tables and sheets. This significantly increases the complexity of the application and leads to some disadvantages.
Disadvantages of relational databases:
- Complexity
For users who maintain the application, it is difficult to understand the complex and multi-layered structures. - Adding new features
Adding features is more difficult because, for example, with cross-references there are more tables and sheets to consider. - Retrieve data
Retrieving data from so many places is inefficient and applications need complex programming codes to deal with it.
Imagine if we transposed this example into the real world and sales representatives had to retrieve names from one file folder, phone numbers from another and addresses from a third folder. You can imagine how complicated, error-prone and slow that would be.
What question do you have about MongoDB?
1.2 How does MongoDB solve the problem?
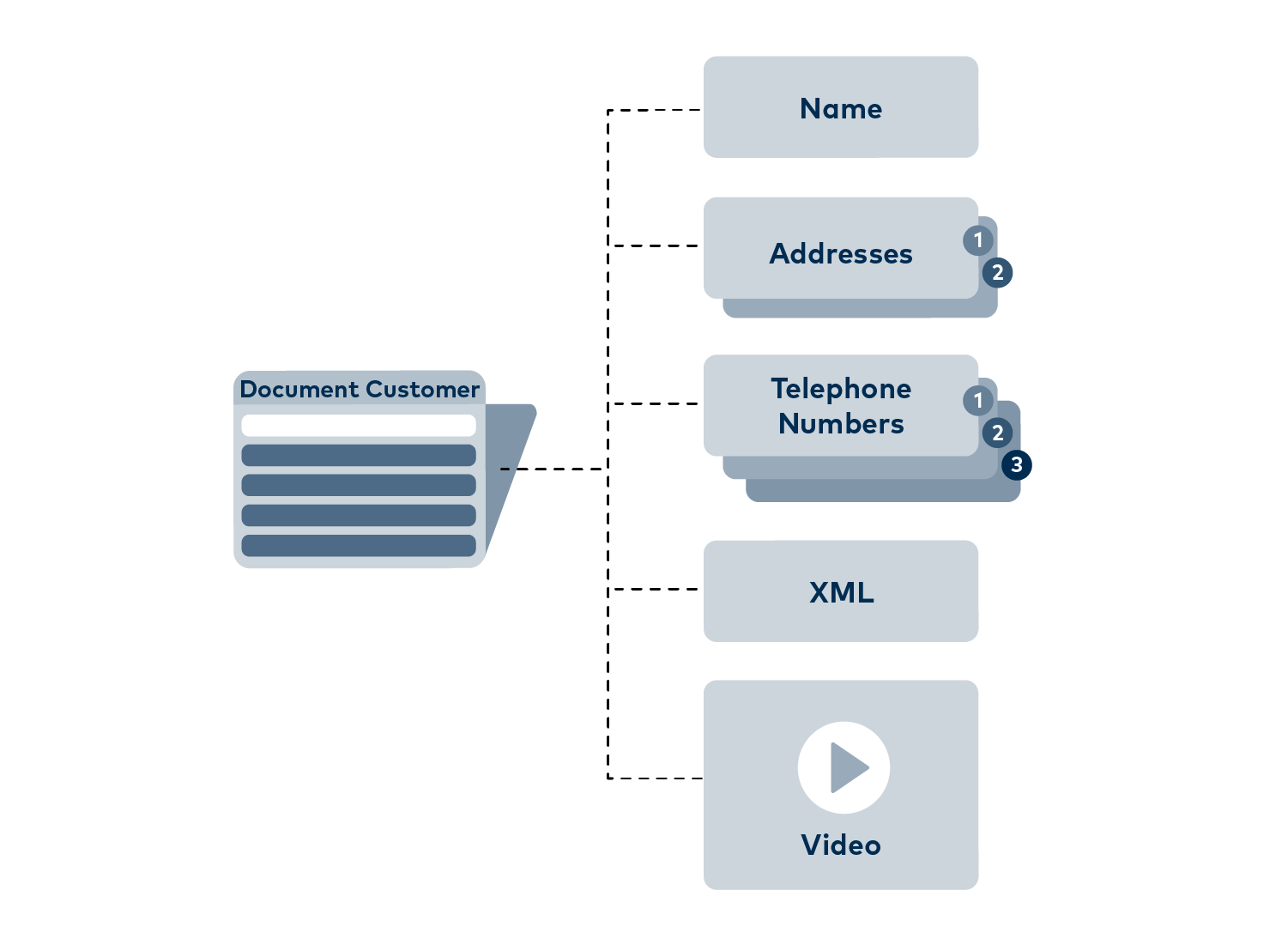
MongoDB now follows a completely different “schema-free” approach. Data is stored in so-called “documents”.
Just like physical customer files in a hanging file, a document can contain two addresses, three phone numbers and other information, such as an individual training video. It can be stored right next to another customer document that contains only a phone number, an address and no orders yet. These documents are not limited to having the same number of column documents or data fields.
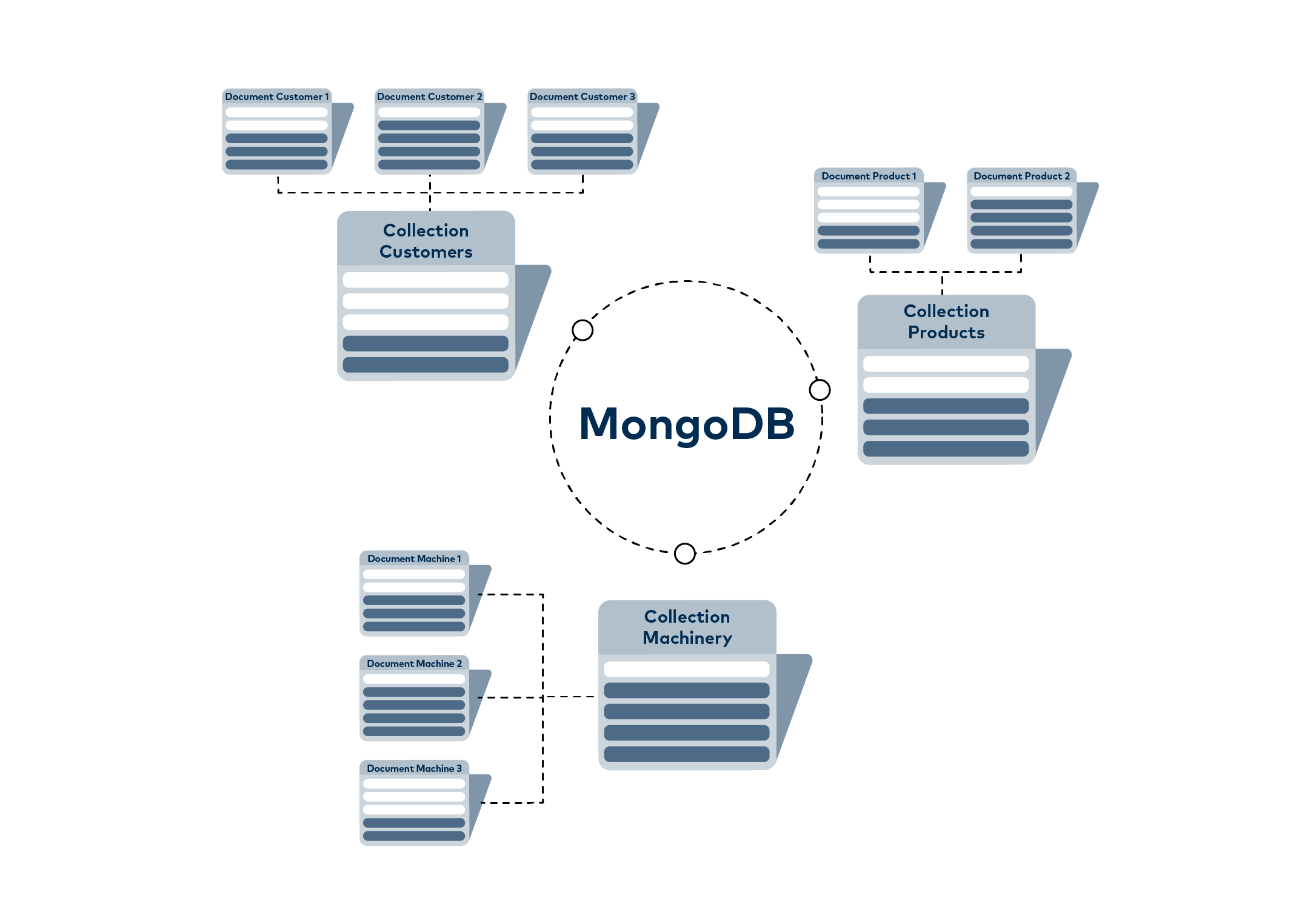
MongoDB groups several documents into “collections”, of which the database can contain several.
IT can process the data structured in this way more efficiently and, of course, these documents are also much easier for people to read. This type of data storage is incredibly beneficial for developers, as they no longer have to adapt their applications to the requirements of the database. With MongoDB, applications can store data in a natural and convenient way. This also means that adding new data is possible without worrying that a simple change could cause database records to become unreadable.
1.3 Differences to traditional databases
In addition to the document model, MongoDB is fundamentally different from traditional databases because its functionality allows MongoDB to coordinate multiple servers to store data.
This makes MongoDB a distributed database and enables it to provide the fault tolerance, scalability as well as data availability features that developers would otherwise have to create themselves and can thus save risks and labour.
- Fault tolerance
To ensure fault tolerance in the work, redundant copies of the same data are kept on different servers. A failure of a single server does not affect the application. - Scalability
MongoDB scales seamlessly to multiple servers to store and process data. So data volume and performance requirements increase. You can simply add more servers instead of upgrading expensive mainframes. This is also ideal for cloud environments where the load is distributed across many computers. - Data availability
Data is available locally near users around the world for quick access.
The combination of the MongoDB document model and the distributed system components gives MongoDB an advantage over relational databases.
In addition, the “Mongo” company also provides management tools that allow database operators to oversee the configuration, monitoring, backup, recovery and updating of MongoDB clusters. This is critical to make MongoDB suitable for the most demanding use cases and for organisations with stringent SLA (Service Level Agreement) and operational requirements.
2. MongoDB in the cloud and as a service
MongoDB was developed for the cloud and has been widely used there for some time.
However, more and more users are also interested in creating their applications with components that are offered as a “service”. To meet this need, “MongoDB Atlas” has been released as a service offering. Atlas allows users to use MongoDB as a service without having to worry about managing the database. MongoDB Atlas is available on the leading cloud platforms AWS (amazon web services), Microsoft Azure and the Google Cloud Platform. This provides the flexibility to choose a public cloud provider without vendor lock-in and without having to rewrite code. These innovations are driving more and more companies to incorporate the MongoDB platform.
3. How to install MongoDB?
The installation of MongoDB is updated regularly and varies depending on the operating system. For this reason, we refer you directly to the official MongoDB documentation, where you will always find the latest installation instructions.
Visit the Getting Started page of MongoDB Community Edition to select the appropriate download and instructions for your system. There you will find detailed step-by-step instructions for Windows, macOS, Linux, and other platforms.
The official documentation ensures that you are always working with the latest installation methods and download links.
How to implement your digitization strategy with MongoDB – we will be happy to help you!
4. FAQ
- What is MongoDB?
MongoDB is a document-oriented NoSQL database. Instead of storing data in tables, it uses flexible, JSON-like documents, allowing dynamic structures without a fixed schema.
- What is MongoDB used for?
MongoDB is used when applications require complex, evolving data structures, for example in web services, mobile apps, big data platforms and real-time analytics.
- How does MongoDB differ from traditional SQL databases?
Unlike SQL systems like MySQL or MariaDB, MongoDB doesn’t use fixed-column tables. It stores documents in collections, allowing greater flexibility in structure.
- When is MongoDB useful?
MongoDB is beneficial for large, variable datasets where you require fast queries and horizontal scalability. It’s often less suitable for highly structured relational data.
- How does MongoDB scale?
MongoDB scales horizontally through sharding: data is distributed across multiple servers, keeping performance high even with large datasets.
5. Summary
The NoSQL database MongoDB was developed as an open source project by the community and is now also used extensively in the industrial environment.
However, MongoDB’s pay-as-you-go model, which also exists, is widely used here, as business-critical applications can rarely do without a fully managed failover and complex recovery options. But the community edition available free of charge at www.mongodb.com is an excellent way to enter the NoSQL world with this database.
Further information
Read here how the OPC Router with the MongoDB Plug-in can access the data of the NoSQL database in read and write mode and supports the handling of replication.
A Telegram Bot is a good way to deliver information from almost every conceivable area whenever you need it.
We point out precisely this special mode of operation in an article in our Knowledge Base “Technology” and also provide instructions on how to create a Telegram Bot yourself.
OPC UA – What is it actually?
OPC UA standardises access to devices, machines and other systems in Industrie 4.0 and thus enables manufacturer-independent data exchange. You can find an overview of the terms and functionality of the most important communication protocol for Industry 4.0 and the IoT in our Knowledge Base.
Further interesting articles on the topics of Industry 4.0, cloud, technology, alerting and practical application examples as well as case studies can be found in our Knowledge Base.

