Middleware and its relevance for industry
Implementing digital transformation in everyday business involves numerous challenges that a middleware solution can help to overcome. The hardware and software systems used in companies often come from different manufacturers and tend to be incompatible. Therefore, it is more urgent than ever that all these systems in the company work together seamlessly by communicating smoothly with each other. That is where middleware comes in handy. In our article, you will learn everything you need to know about middleware in industrial use and what significance the use of middleware has for digital transformation in the industry.
Contents
- Definition middleware
- What does a middleware do?
- Functionality
- Connectable system components
- Importance and scalability
- Advantages of middleware
- Requirements for use
- Expansion or change of the system landscape
- Middleware alternatives
- Middleware requirements
- Practical areas of application in industry
1. What is middleware?
Middleware is an elementary software that connects two separate applications. In the industrial environment, the field level (OT), consisting of machines, devices, and controls, is connected to higher-level systems on the IT level, such as databases, ERP, or cloud systems. This connection is bidirectional and can therefore start at the field level and end at the IT level, and vice versa from the IT to the OT.
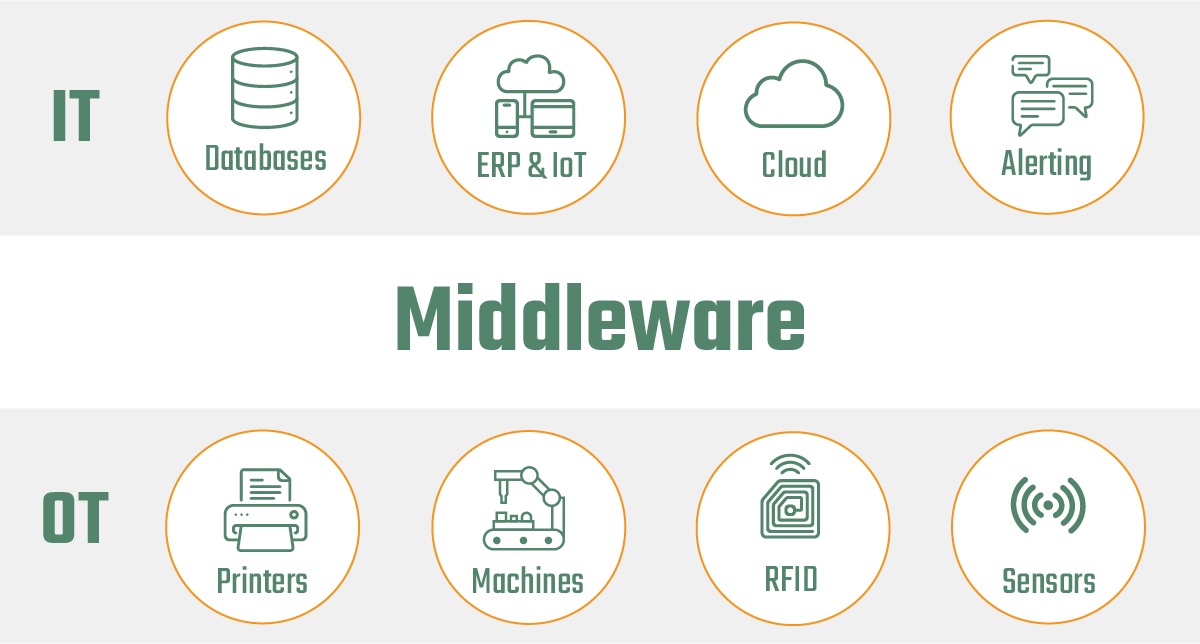
The connection enables distributed devices and applications to communicate and closes the system gaps that arise due to the heterogeneous system landscape. Middleware thus establishes an exchange of data between the various systems, which are often isolated in practice.
2. What does a middleware do?
As software, middleware ensures that all systems in a company can communicate with one another by using the exchange of data. In the process, middleware platforms and systems make it possible to link several applications and systems simultaneously.
Middleware creates a homogeneous structure from various heterogeneous applications in a system landscape, such as IT systems, devices, and machines.
However, the different systems are often incompatible with another and do not speak the same language, so a middleman is needed. That is precisely the task performed by middleware. It transforms data and makes it available in the required language (standard) so that the respective systems can understand data from other systems and vice versa. Therefore, middleware platforms are also known as intermediaries or software with an intermediary function.
What question do you have about an industrial middleware?
3. Functionality
Connection via interfaces
All systems and applications in a system landscape connect to the middleware. This connection takes place via an interface that the respective device or system to connect brings with it. Via these interfaces, the middleware ensures that each system and each application receive the data in the format it can read and process.
Structure of a data transfer
The middleware takes data from a data source and transforms it. It converts the data in a way that a higher-level system, such as a database, receives a data point from a controller in a format that it can read and process. That creates a connection from OT to IT. This connection enables a consistent and automatic data transfer. This data transfer can take place both without standardized communication and based on a communication standard such as OPC UA or JSON.
4. Which system components can a middleware connect?
Middleware software can interconnect all systems and applications that have an interface. This interface is a prerequisite for the connection to work. In OT, for example, sensors, machine controls, barcode readers, scanners and label printers can be connected to higher-level IT systems using middleware and the proper interface. In IT, all system components such as servers, databases, cloud systems, ERP and MES systems can be networked with other IT or OT system components using middleware if they also have the correct interface.
5. What are the reasons of using in the company?
Why middleware is important
Figuratively speaking, middleware is like a bridge builder in a company and an intermediary between all existing systems and applications. Where there are communication gaps without the use of middleware, processes are not automatic and data transfers are not transparent, the quality, efficiency and, in the long term, the success of a company suffer. A sustainable digitization strategy thus becomes a distant prospect.
Middleware creates the foundation for building an Industry 4.0 structure in the company and lays the groundwork for digital transformation.
The use of middleware creates a homogeneous structure for all systems and applications used throughout the company, resulting in uniform and efficient communication.
Possibility of vertical and horizontal scaling
Middleware software offers the possibility of scaling horizontally and vertically providing companies with essential opportunities for growth. Horizontal scaling occurs when there is the possibility of always being able to add more system components within a system landscape. Vertical scaling opportunities arise when additional resources like servers or databases that increase computing power get built into the system landscape. If the new components have appropriate interfaces for connection, both scaling are easily possible with middleware.
What question do you have about an industrial middleware?
6. What are the benefits of using middleware?
Networking applications and software components with each other and creating communication between distributed systems, devices and applications brings numerous advantages:
- Networking: Devices, machines and controls at the OT level and systems at the IT level no longer work in isolation from one another but are networked together.
- Digitalization: Through networking, middleware contributes significantly to increasing the digitization rate in the company. Providing this as a basis, it continues to promote enterprise-wide digital transformation.
- Automation: The connection and networking of distributed system components offers the possibility of automated and transparent data exchange, which is significantly less error-prone and therefore more efficient.
- Process optimization: When all system components are interconnected and all data available in a company is captured and analyzed, this forms the basis for optimizing workflows and processes.
- Increasing efficiency: Transparent data transfers and optimized processes are accompanied by an increase in efficiency because resources can be better controlled and used. That also results in other benefits such as increased productivity, reliability, cost reduction and quality assurance.
- Process reliability: Transparent data transfers and efficient processes mean that disruptions in production, for example, can be rectified quickly or do not occur at all.
- Reduction in complexity: A homogeneous system landscape is less complex and requires less administrative effort.
7. What are the requirements for using?
The most significant prerequisite for the use of middleware is independence. Middleware should be independent of the network details in which it is used, along with the protocols for data exchange. Furthermore, the independence of operating systems is relevant so the middleware can function across platforms. Another requirement is independence from specific languages. Suitable middleware must be compatible with all the required languages in the existing system landscape. Finally, it is important that the middleware works in the background and that nothing is noticed at the application level about how many individual components the system consists of.
8. What happens in the event of extensions or changes in the system landscape?
In practice, it is common for a heterogeneous system landscape to be changed or expanded. If data transfer takes place with the help of middleware, the core of the transfer remains the same. That is entirely independent of whether a new system component is added to the existing landscape or replaced. That means that the current system landscape can be changed or expanded at will, both in OT and IT, creating the opportunity for scaling.
Middleware makes it possible to expand or change a system landscape at will – the data transfer remains at its core.
For example, it is possible to switch from one control system to another without further ado. In the same way, it is also possible to integrate a machine into another machine park without any problems.
9. What are the alternatives to middleware?
Middleware vs. API
An API (Application Programming Interface) is a programming interface offering, similar to a middleware, the possibility to network applications and let them communicate together. As the name implies, the use of an API requires programming. Through an API, programmers can connect systems using commands, functions, protocols, and objects.
Thus, the API is also a way to connect system components to each other. In contrast to an API, a middleware relies on many interfaces to provide more flexibility in the ability to connect systems.
Middleware vs. protocols
Protocols are a central element of communication between systems and applications. They define the way in which information is exchanged. These include, for example, rules, formats, parameters and properties of data that ensure complete, error-free and efficient data transfer. Examples of IT protocols are the HTTP, TCP or IP protocol.
As with API, each protocol represents a way of regulating communication between two system components. Middleware, on the other hand, bundles many protocols and offers the advantage of flexibility in linking individual system components.
10. What are the requirements for good middleware?
When choosing the appropriate middleware, there are several criteria that should be checked. In addition to the prerequisite of independence from protocols, operating systems, languages, and platforms, as well as background operation, there are several further criteria that should be considered in the selection process:
- Security: security is a key consideration where a lot of data is collected and transferred. Sensitive information such as customer or production data needs protection against access by unauthorized persons. Middleware must always meet the highest security standards and guarantee security.
- Scalability: A middleware should be able to be implemented in a scalable manner. Adding new system components at the IT and OT level should be possible with a middleware without much effort.
Connectivity diversity: For maximum flexibility and to map the heterogeneous system landscape in the best viable way, middleware should provide an API and offer the option of integrating different protocols. - Continuous further development: The use of middleware should support a company’s long-term digitization strategy. It is particularly important that the software is constantly optimized and further developed, and that regular updates and support are offered.
- Programming effort: If a company has only limited resources for programming interfaces, or none, this is an important criterion when selecting the right middleware. There is middleware software, such as OPC Router, which enables the connection of individual system components on a graphical user interface and for which programming knowledge is not a prerequisite for use.
How to implement your digitalization strategy with an industrial middleware – we are happy to help!
11. What are practical applications of middleware in industry?
Its universal functionality allows middleware to be use across industries and use cases and thus supports digital transformation. In the following, we explain two practical examples from industry in which processes and data transfers are controllable with the help of middleware.
Providing the controller (PLC) with data and decisions
In automation, controllers coordinate complex machine sequences and production processes. During a production chain, many decisions depend on data from other systems. An example is customer order data, which varies from customer to customer and is stored in a database or an ERP system. It is possible by using middleware to automate the transfer of this data to the PLC. The middleware captures the customer order data and sends it to the PLC to start production. Based on defined communication standards, for example, OPC UA, a middleware can communicate with the machine. This communication eliminates the need for manual entry of order data directly in the OT and ensures fast and efficient production.
Receiving alarms and thus keeping an eye on production
Machine data acquisition and the evaluation of this data are essential components for efficient production. With the help of middleware, data from a control system can be linked to IT. In industry, a decisive advantage here is alarming. Middleware receives data from the machine, analyzes it in real-time and can send notifications based on this data. For example, the middleware can be used to send an alert to the responsible employee when a production job has been completed. The employee can then transfer the next order from the system to the machine and start production for the next product. Limit values on the machine can also be transferred to the IT system via alarms. For example, if temperatures in a machine are too high, employees can be informed in real-time and can then react and initiate countermeasures. In this way, production stops can be prevented, and downtime avoided.
Further information
Discover more about Industry 4.0 – the fourth industrial revolution – with our article. It is characterized by many stakeholders in industrial production that are networked and interact with each other. That includes customers, products, machines, software systems and people involved in production.
Interfaces serve as connection points between different systems and applications, ensure seamless integration of these components and are omnipresent in industry. Read our article “What are interfaces?” to find out why they play a crucial role in today’s networked world and in industry.
OPC UA is one of the most important communication standards for Industrie 4.0 and the IoT. Our practical introduction “What is OPC UA?” gives you an overview of what is important for practical use and provides you with the necessary orientation for your project among the many technical terms.
Further interesting articles on the topics of Industry 4.0, cloud, technology, alerting and practical application examples as well as case studies can be found in our Knowledge Base.